How Blockchain Is Innovating Intellectual Property Protection
Challenges In Protecting Intellectual Property (IP) Intellectual Property (IP) protection in the digital age has been a major challenge in the modern world. As the internet has grown and content has become easier to share online, copyrighted material such as music, artwork, writing, and inventions are increasingly vulnerable to theft. The speed and complexity of the digital age has left traditional IP protection systems in the dust.
Step in to blockchain technology, a novel tool that could be a game-changer for the way intellectual property rights are managed and protected. Originally made for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, the additionally alluring attributes of blockchain transparency, security, and immutability are being researched for protecting imaginative works and developments.
This article explores how blockchain transforms IP protection and the possible benefits it can offer, its many challenges, and what the future may hold for its creators, innovators and firms.
What Is Intellectual Property (IP)?
So before we dive into what role can blockchain play in protecting IP, we need to understand what is intellectual property. What do we mean by intellectual property? OK, Intellectual property is any creation of the mind, e.g.:
- Copyrights — Protects literary, artistic, and musical works. Cookie Policy.
- Patents: Excludes others from making, using, or selling their inventions for a certain period of time.
- Trademarks: Safeguards names, logos & slogans.
- Trade Secrets: Their proprietary business information for when they are ahead of competitors.
It shelters the creator within its limitation, but permits other forms of innovation at its core. But claiming these rights, especially in the digital universe, can be fraught and costly.
What is Blockchain Technology?
In short, blockchain is a distributed, digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. Each transaction is recorded in a “block,” which is linked to the previous block, forming a “chain.” This technology ensures that once the information is written, it cannot be tampered or deleted, provided all the relevant parties agree.
Features Solving IP-Preservation Problems Blockchain's awesome role in IP protection is enabled by many features such as;
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to all network participants which creates a public record.
- Security: Data on the blockchain is encrypted and immutable.
- Decentralization: No one entity is pulling strings on the data.
- Immutability — After a transaction is posted it cannot be changed, hence ensuring veracity.
As a result, blockchain can be very useful in ownership monitoring by machines, as well as proving intellectual property.
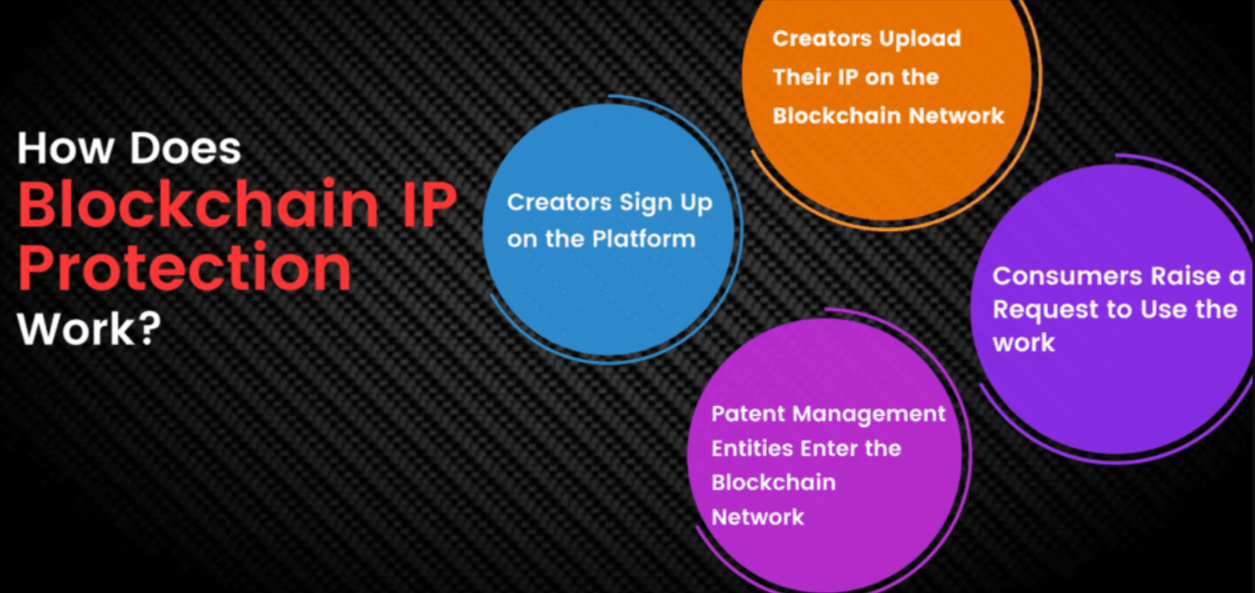
THE WAY BLOCKCHAIN ENHANCED THE PROTECTION OF IP
Explore Here’s How Blockchain Can Change The Way If Intellectual Property Management
1. Ownership and Authenticity Verification
One of the biggest challenges creators face is proving ownership of their work. Indexed in the blockchain, creators are able to register their IP, and it offers timestamped, immutable proof of authorship.
For example, an artist can create a mint of their digital work on a blockchain network. A digital certificate will be issued, proving when the artwork was created and who its rightful owner is. It makes it easy to resolve disputes and verify authenticity.
2. Smart Contracts for Licensing
Similarly, smart contracts can be automated to make licensing agreements seamless. These are self-automated contracts with rules embedded in the program code. The contract automatically executes itself if certain conditions are met without needing a middleman.
For example, a music track can be licensed by a musician through their song smart contract. The license when bought, and rights of use and payment, transfer automatically within a blockchain system. This model allows content creators to be paid without the use of intermediaries.
3. Transparent Royalty Payments
The problem with this system is that, royalty payments are opaque and often indecipherable. Blockchain can automatically and accurately track on how many pieces of content are used and distribute royalties.
For instance, a songwriter is able to use blockchain to know how many times her song has been streamed. Payments can then be distributed automatically in real time using smart contracts, which means that payments are fair.
4. How to Avoid Fakes and Piracies
Blockchain can help protect brands and products from counterfeiting. Companies can use blockchain to create certificates of authenticity for the products they manufacture.
A luxury brand could issue each item it sells with a custom blockchain code. That will help customers verify its authenticity if they scan the code, reducing the likelihood of purchasing counterfeits.
5. Rapid Filings of Patents and Trademarks
Filing the patents and trademarks can take long processes and costly. Blockchain can streamline this process through a transparent and decentralized platform for registrations.
This can allow the innovators to prove the date when they invented and register their ideas in a chronometer on a digital ledger protected by blockchain. This can help crystallize a clear record of the date of something’s invention and its ownership, streamlining and securing the patent process.
Benefits to Using Blockchain and Intellectual Property Ownership
Benefits of using the blockchain to develop IP management include:
1. Enhanced Security
Blockchain’s tamper-proof mechanism ensures that ownership/ licensing records are immutable and cannot be manipulated.
2. Reduced Legal Disputes
Plain and time-stamped ownership proofs can make dispute resolution easier and fairer.
3. Fair Compensation
Every time one of its creations is utilized, smart contracts allow it automatic and equitable payment.
4. Global Accessibility
As it operates upon a decentralized network, creators across the globe can register their intellectual property rights on the blockchain without relying on local legal systems.
5. Cost-Effective
This will reduce the costs of legal and administrative fees, associated with registering and protecting intellectual property, as blockchain gets rid of intermediaries.
Challenges Of Blockchain In IP Protection
While blockchain is a promising technology, it remains to be determined whether this is useful in the IP protection arena at large:
1. Legal Uncertainty
This has led to a situation where there is little progress on clear legal regulations addressing blockchain-based IP registrations in many countries.
2. Scalability Issues
The blockchain becomes slower and less efficient the bigger the platform as platform users are ever-increasing.
3. Energy Consumption
Other blockchain systems, such as Bitcoin, use ginormous amounts of power, with environmental implications.
4. Technical Complexity
How creators and businesses can apply the benefits of blockchain technology is still a very new concept and can be no small feat for many.
5. Enforcement Challenges
Blockchain does not substitute the need for legals step any most of those still liaise with existing legal framework a slow process that can be inconsistent even within jurisdiction.
Real-World Examples of IP Protection via Blockchain
Several blockchain(s) based platforms and companies are already protecting various forms of intellectual property:
1. Ascribe
A place for artists to encrypt and record their art on the blockchain, assuring ownership and how their art can be used.
2. Po.et
A ledger-based platform to help writers and publishers to timestamp their content and record irrefutable proof of authorship
3. VeChain
A Blockchain based anti-counterfeiting solution catering mainly to the luxury and pharmaceutical industries.
4. KodakONE
It is a blockchain based service that assists photographers to register, license, and track their images.
The Future of Blockchain in Intellectual Property Protection
As blockchain technology matures, it will continue to develop and play a larger role in IP protection. Here are some trends to watch for:
1. Integration with AI
Blockchain technology could be used to state a public ledger of IP Rights infringements, whereas AI-based software could be employed to monitor potential IP infringements.
2. Global Standardization
Governments and international organizations may develop standardized blockchain systems for IP protection around the world.
3. Decentralized Marketplaces
That could foster peer-to-peer, blockchain-based marketplaces where creators license and sell works directly to consumers.
4. Real-Time IP Monitoring
One possible solution could be using blockchain-based platforms to track the usage of intellectual property across the web in real time.
Conclusion
Amid such challenges, blockchain technology has emerged as a potential solution for the rising threat to intellectual property in the digital space. It is a game-changing invention in blockchain technology on the most official level and means in more advanced solution.
There are still obstacles to navigate - acquiring legal standing and getting over the technical hump - but the outlook is promising. This will equip creatives with even better tools as more industries begin to transition toward blockchain-based solutions to protect their IP, meaning they will receive the proper credit for work done and proper payment as industry continues to move in a more digital direction.
In doing so we enter a future in which the works of the mind are more safe, accessible and respected more than ever before in history.